3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is an exciting technology that has transformed the way we create objects. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods that often involve cutting away material, 3D printing builds items layer by layer. This process allows for greater design flexibility, making it possible to produce complex shapes that would be difficult or impossible to achieve using conventional techniques.
The heart of 3D printing lies in its ability to create three-dimensional objects from digital files. To start the process, a designer creates a computer model using specialized software. This model is then sliced into thin horizontal layers by slicing software, which prepares it for the printer. Once the printer receives the sliced file, it begins to deposit or fuse materials in a precise manner, gradually building up the object from the ground up.
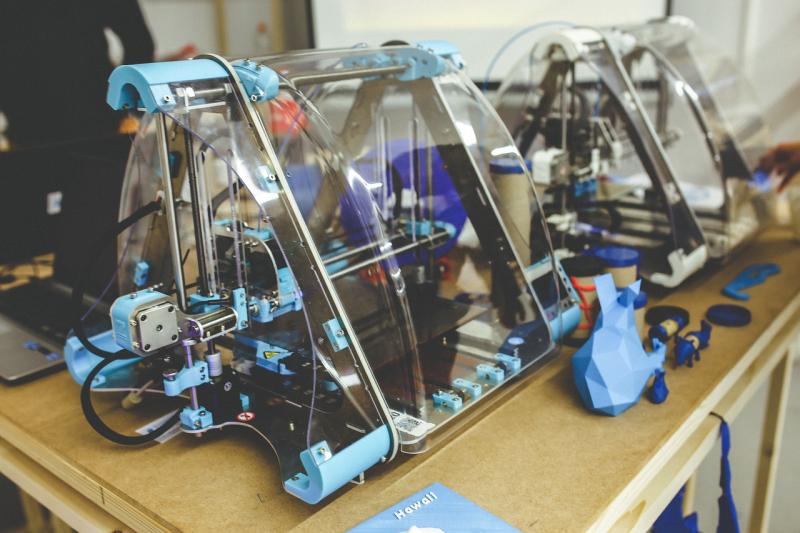
There are several types of 3D printing technologies available today. Some popular methods include Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), which uses thermoplastic filament, and Stereolithography (SLA), which utilizes a liquid resin that hardens when exposed to light. Each technology has its own advantages and is suited for different applications, from prototyping to final product manufacturing.
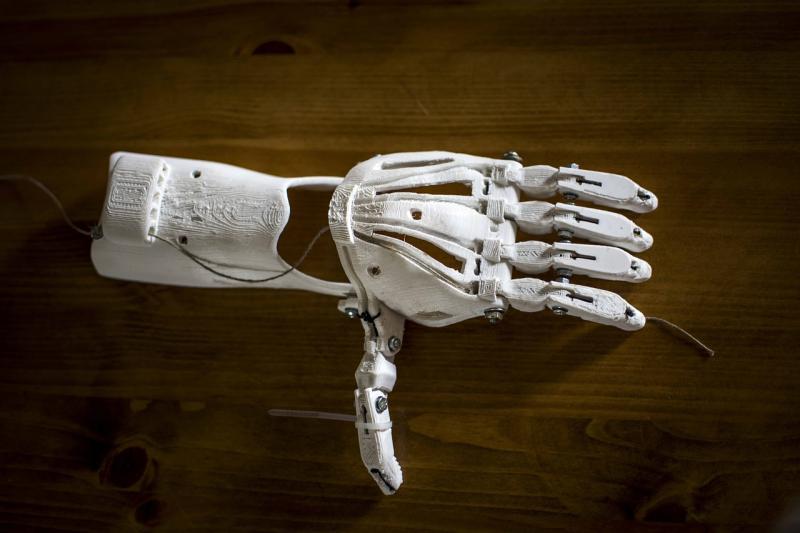
One of the most exciting aspects of 3D printing is its accessibility. As the technology has developed, more affordable printers and materials have become available, enabling hobbyists and small businesses to take advantage of 3D printing. With a little creativity, anyone can dive into this fascinating world, whether it’s making custom tools, unique gifts, or even artistic creations.
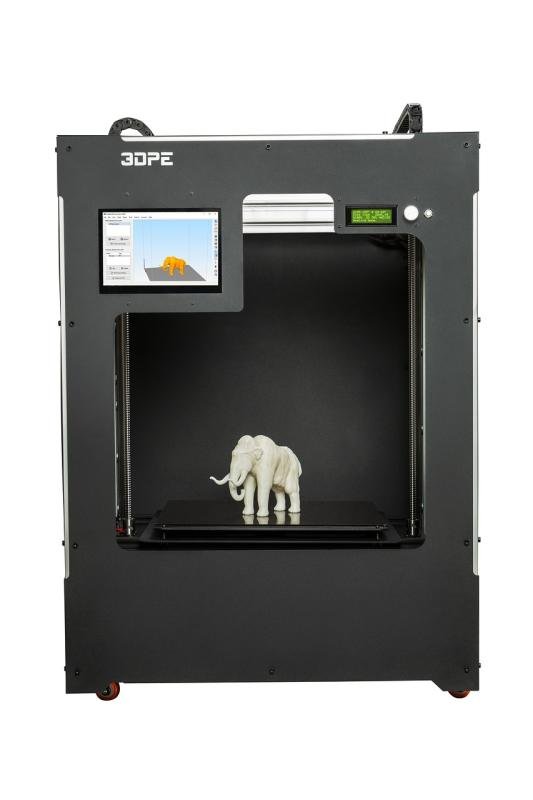
Choosing the Right 3D Printer
3D printers come in various types, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) printers are popular among beginners due to their affordability and ease of use. They work by melting plastic filament and layering it to create objects. On the other hand, Stereolithography (SLA) printers offer higher precision and detail, making them a good fit for detailed projects, but they tend to be pricier and require more maintenance.
Another important factor to consider is the printer's build volume. This refers to the maximum size of the object you can print. If you plan to create larger items, look for a printer with a spacious build area. Additionally, consider the materials you want to use. Some printers are compatible with a wide range of filaments, while others may restrict you to specific types. Understanding material options will help you achieve the results you desire.
Lastly, don't overlook the printer's community and support resources. A strong community can provide valuable insights, troubleshooting tips, and ideas for your designs. Brands with active forums or customer support can make your 3D printing journey smoother and more enjoyable. As you explore your options, take your time to research and compare different printers to find the one that perfectly fits your unique needs.
Materials for 3D Printing Explained
3D printing opens up a world of creativity and innovation, and the materials used play a crucial role in the final product. There are several types of materials that you can use for 3D printing, each with its own unique properties and applications. The most common material is plastic, particularly a type called PLA (Polylactic Acid). PLA is popular among beginners because it is easy to use, biodegradable, and comes in a variety of colors.
An alternative to PLA is ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene), which is known for its strength and durability. ABS is ideal for printing items that need to withstand heat and stress, such as toys or functional parts. However, it requires a heated bed during printing to prevent warping. As you gain experience in 3D printing, you might explore more advanced materials like PETG, a strong and flexible plastic, or TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane), which is rubber-like and great for creating flexible parts.
In addition to plastics, you can also experiment with metal and resin materials. Metal 3D printing typically requires specialized and expensive equipment, but it’s perfect for creating strong and precise parts used in industries such as aerospace. On the other hand, resin printing allows for high-detail models and is often used for artistic and intricate designs. Resin can be more challenging to work with and requires post-processing, but the results can be stunningly detailed.
Each material has its own set of characteristics, so it’s important to consider what you want to create. Whether you’re after strength, flexibility, or intricate detail, there’s a material out there to meet your needs. As you get comfortable with 3D printing, don’t hesitate to try out different materials to see what works best for your projects!
Basic 3D Printing Techniques to Know
3D printing is an exciting technology that allows you to turn digital designs into physical objects. For beginners, it's essential to get familiar with some basic techniques that will make your 3D printing journey smoother and more enjoyable. Here are a few techniques worth knowing.
One of the most fundamental techniques is Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM). This method works by melting plastic filament and layering it to build a 3D object. It's popular for home users because it is affordable and compatible with a wide range of filaments. The process is relatively simple: you load the filament into the printer, heat the nozzle, and watch as the printer creates your design, layer by layer.
Another important technique is Stereolithography (SLA), which utilizes a laser to cure liquid resin into solid forms. SLA printers can produce highly detailed objects, making them perfect for intricate designs like jewelry or miniature models. However, the process can be messier and generally requires post-processing, such as washing and curing the printed object, which is essential for achieving the best results.
Besides printing methods, it's also crucial to understand the significance of bed leveling. Bed leveling ensures that the first layer of your print adheres properly to the print surface, which is vital for a successful outcome. A poorly leveled bed can lead to warping or even failed prints, so taking a moment to calibrate your printer before starting a project can save you time and frustration.